Comprehensive Guide to SSM-Based Examination and Enrollment Management System for Computer Science Graduation Projects
For computer science and software engineering students, a graduation project based on an SSM (Spring, Spring MVC, MyBatis) framework for an Examination and Enrollment Management System represents a robust and practical application of modern web technologies. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of such a project, covering its core components, extended implementations (including Android, Spring Boot, and WeChat Mini Programs), and essential resources for successful completion.
Project Core: The SSM Backend
The foundation is a Java-based web application using the SSM framework. This system typically manages core functionalities like:
- User Management: Roles for administrators, teachers, and students/ applicants with distinct permissions.
- Examination Management: Creating exams, setting schedules, defining subjects, and managing question banks.
- Enrollment Process: Handling applicant registration, document submission, fee payment, and admission decisions.
- Result & Analytics: Publishing scores, generating reports, and providing statistical dashboards.
- Notification System: Sending alerts about deadlines, exam schedules, and results.
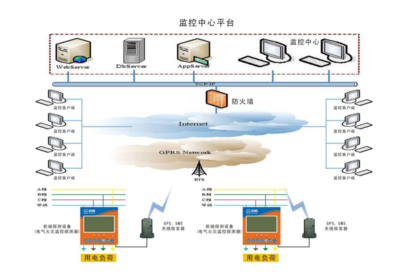
This backend serves as the central data hub, providing RESTful APIs for various client applications.
Extended Application Platforms
A modern, full-featured project often extends beyond a simple web interface:
- Android Application: A native Android app (written in Java/Kotlin) provides mobile access for students to register, view schedules, check results, and receive push notifications. It consumes the backend APIs.
- Spring Boot Refactoring: While SSM is traditional, refactoring the backend to Spring Boot is highly recommended for its simplicity, embedded servers, and convention-over-configuration approach, making deployment and development more efficient.
- WeChat Mini Program: Developing a companion Mini Program offers immense accessibility within China's dominant social platform. It can replicate core mobile functions with a lightweight, fast-loading experience.
- Python Management Tools: Auxiliary scripts in Python can be developed for data analysis (e.g., using Pandas for enrollment trend analysis), automated report generation, or system monitoring, showcasing interdisciplinary skills.
Key Project Artifacts and Resources
A successful graduation project requires more than just code:
- Source Code & Database: A well-structured, documented codebase and SQL scripts for database schema creation and sample data are fundamental.
- Software & Tools: The project typically requires:
- Backend: JDK, Maven/Gradle, IntelliJ IDEA/Eclipse, MySQL/PostgreSQL, Tomcat.
- Android: Android Studio, Android SDK.
- Mini Program: WeChat Developer Tools.
- Opening Report (开题报告): This crucial document outlines the project's background, objectives, significance, technical feasibility analysis, research methodology, implementation plan, and expected outcomes. It sets the roadmap for the entire project.
- Project Thesis/Dissertation: The final report detailing system analysis, design (UML diagrams like Use Case, Class, Sequence diagrams), implementation, testing, and conclusions.
Finding Project Resources
Numerous online platforms and university repositories offer project titles, source code, databases, and reports for reference and learning. Common channels include GitHub, Gitee (码云), CSDN blogs, and specialized graduation project websites. It is critical to use these resources for learning and inspiration only. Direct copying constitutes plagiarism and undermines the educational purpose. The goal is to understand the architecture, solve similar problems, and then build your own unique implementation.
Implementation Roadmap
- Requirement Analysis & Planning: Define the specific scope (e.g., will it include online payment? face recognition for exam authentication?). Write a detailed opening report.
- System Design: Design the database E-R diagram, define API interfaces, and plan the system architecture (layered architecture: controller, service, dao).
- Backend Development: Build the SSM/Spring Boot backend first. Implement entities, mappers (MyBatis), service layers, and REST controllers.
- Frontend & Client Development: Develop the web frontend (using JSP, Thymeleaf, or a frontend framework like Vue.js for a separated frontend). Concurrently, develop the Android app and/or WeChat Mini Program.
- Integration & Testing: Integrate all clients with the backend APIs. Perform unit testing, interface testing, and system testing.
- Deployment & Documentation: Deploy the system on a server or cloud platform. Complete comprehensive project documentation and thesis writing.
By tackling a multi-platform SSM-based Examination and Enrollment Management System, students demonstrate a full-stack understanding of enterprise application development, from backend API design to multi-client integration, which is highly valued in the software industry.
如若转载,请注明出处:http://www.ds57.com/product/287.html
更新时间:2026-02-25 13:11:09